<SwiftUI for Absolute Beginners>读书
Contents
SwiftUI 原则
四大原则
- 声明式(
declarative) - 自动化 (
automatic) - 组合 (
composition) - 一致 (
consistent)
#SwiftUI 背后的 Swift 5.1
不透明的返回类型 (opaque return type)
import Cocoa
protocol P {}
extension Int: P {}
extension String: P {}
func add1() -> some P {
return "some value"
}
func add2() -> some P {
return 110
}
let res: P = add1()
let res2: P = add2()
print(res)
print(res2)
函数所有返回路径上返回的值应该是相同的具体类型, 而不能是不同的类型
这不同于返回 协议(protocol) . 只返回协议类型的话, 可以是协议的任一类型, 而 opaque 则返回的是同一类型, 虽然也不确定是哪一个类型.
##从单一表达式函数隐式返回
简单地说, 就是从一个只有一个表达式的函数中不需要添加 return 关键字来返回. 例如
func add(num: Int, num2: Int) -> Int {
num + num2
}
函数构建器
简单说它是特殊的带注解的函数, 用于组件序列隐式地构建值. 这些组件通常采用语句和表达式的形式, 它们一起生成单一值. 这是基于构建器 设计模式.
let cell = StandardCell()
.useTitle(cellData.title)
.useSubtitle(cellData.subtitle)
.useImage(cellData.image)
.build()
特定领域语言 DSL
构建器也特别适合用于 DSL
属性包装器 property Wrappers
import Cocoa
@propertyWrapper
struct Capitalised {
private var value: String
init(wrappedValue value: String) {
self.value = value.capitalized
}
var wrappedValue: String {
get { value }
set { value = newValue.capitalized }
}
}
struct User {
@Capitalised
var firstName:String
@Capitalised
var lastName:String
}
View 和 Controls
在 SwiftUI 中, 几乎所有东西都是一个 view , 这不同于传统的 Objective-C 和 UIKit 的 view. 称为 view , 不同于 iOS 中的 UIView 或 MacOS 中的 NSView , 它不同一个 struct 或 class , 实际上, 它是 protocol
几乎所有符合 View 协议的对象, 都有一个关联类型变量称为 body , body 它再次返回一个 View.
修改器 modifiers
Text
struct ContentView: View {
var body: some View {
Text("Hello, World! 你好, 世界! 修改一下咯.")
.background(Color.red)
.frame(maxWidth: .infinity, maxHeight: .infinity)
}
}
Images
import SwiftUI
struct ContentView: View {
var body: some View {
Image("fuck")
.frame(width: 800,
height: 800,
alignment: .center)
}
}
struct ContentView_Previews: PreviewProvider {
static var previews: some View {
ContentView()
}
}
Image 名字
fuck, 是由在Assets.xcassets里的资源名来决定的.
Buttons
struct ContentView: View {
var body: some View {
Button("点我") {
// handle
print("点击事件...")
}
}
}
Toggle
struct ContentView: View {
@State var isOn = false
var body: some View {
Toggle(isOn: $isOn) {
if isOn {
Text("开启中....")
} else {
Text("关闭中....")
}
}
}
}
TextField / SecureField
struct ContentView: View {
@State var name = "Unknown"
var body: some View {
TextField("input your name", text: $name){
print("你输入的是 \(self.name)")
}
}
}
Slider
struct ContentView: View {
@State var progress = 0.0
var body: some View {
VStack {
Slider(value: $progress, in: -100...100, step: 10)
Text("progress is \(progress)")
}
}
}
Stepper
struct ContentView: View {
@State var steps = 0
var body: some View {
Stepper("Steps \(steps)", value: $steps, in: 0...100)
}
}
Picker
struct ContentView: View {
@State var college = 0
var unis = ["JCU", "CQU"]
var body: some View {
Picker(selection: $college, label: Text("Hello label"), content: {
ForEach(0..<unis.count) { uni in
Text(self.unis[uni]).tag(uni)
}
})
}
}
DatePicker
struct ContentView: View {
@State var whensTheDate = Date()
var unis = ["JCU", "CQU"]
var body: some View {
DatePicker("When is the big day?",
selection: $whensTheDate,
in: Date()...,
displayedComponents: [.date, .hourAndMinute])
}
}
NavigationView
struct ContentView: View {
var body: some View {
}
}
TabView
struct ContentView: View {
var body: some View {
TabView{
Text("First Controller View")
.tabItem({Text("first")})
Text("Second Controller View")
.tabItem({Text("second")})
}
}
}
Stacks
HStack
struct ContentView: View {
var body: some View {
HStack {
Text("Hello")
Text("World")
}
}
}
VStack
struct ContentView: View {
var body: some View {
VStack {
Text("Hello")
Text("World")
}
}
}
ZStac
struct ContentView: View {
var body: some View {
ZStack {
Text("Hello")
Text("World")
.offset(x: 0, y: 20)
}
}
}
Decorators
Spacer
struct ContentView: View {
var body: some View {
VStack { Text("Hello")
Spacer()
Text("World") }
}
}
Divider
struct ContentView: View {
var body: some View {
HStack { Text("Hello")
Divider()
Text("World") }
}
}
Alert
struct ContentView: View {
@State var showAlert = false
var body: some View {
Button("Show Alert") {
self.showAlert = true
}.alert(isPresented: $showAlert) {
Alert(title: Text("Alert Box"),
message: Text("This is our first Alert Message"),
dismissButton: .default(Text("OK")) )
}
}
}
List
struct ContentView: View {
var body: some View {
List(0..<50) { item in
Text("Item # \(item)")
}
}
}
Section
struct ContentView: View {
var body: some View {
Section(header: Text("Header"),
footer: Text("this is a footer")) {
Text("This is the sections’ contents") }
}
}
Data 和 Combine
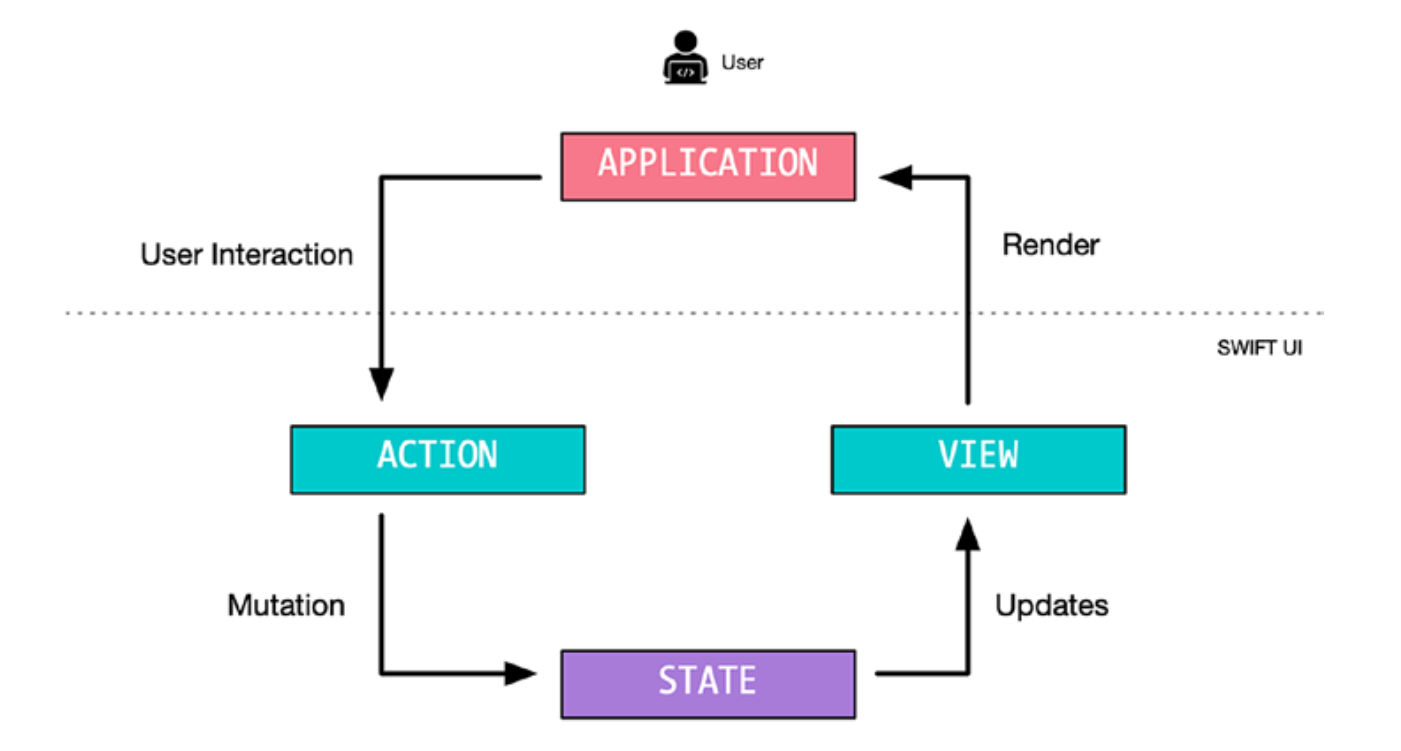
@State
它本质上是一个 Property Wrapper.
表示变量可读写.
更新 View
@Binding
struct ExtractedView: View {
@Binding var booked: Bool
var body: some View {
Button(booked ? "Release" : "Book") {
self.booked.toggle() }
}
}
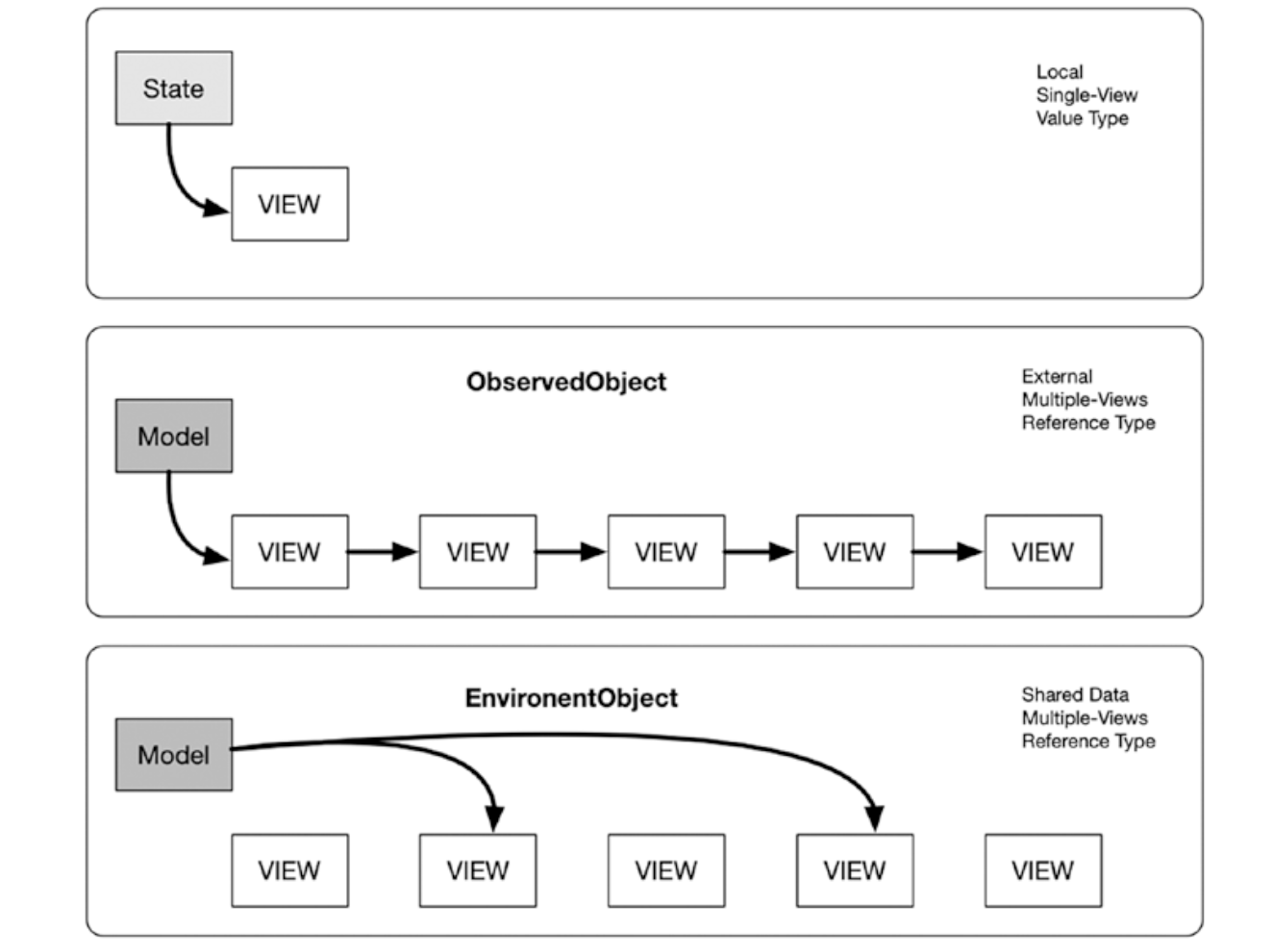
ObservableObject 协议
class BookingStore: ObservableObject {
var objectWillChange = PassthroughSubject<Void, Never>()
var bookingName: String = "" {
didSet { updateUI() }
}
var seats: Int = 1 {
didSet { updateUI() }
}
func updateUI() {
objectWillChange.send()
}
}
struct AnotherView: View {
@ObservedObject var model = BookingStore()
var body: some View {
VStack {
TextField("Your Name", $model.bookingName)
Stepper("Seats : \(model.seats)",
value: $model.seats, in: 1...5)
}
}
}
State Vs Bindable
@State 是 view 本地的 (local). 即数据是被 View 本地持有的. 由于它是本地存储的, 所以它是一个`值类型(value type) 由框架 Framework 自动管理.
@ObservableObject 是在其他外部 View 的, 并没有保存在本地 View. 它是一个引用类型(reference type) . 它并不保存在本地, 只是简单的一个引用. 由开发者管理. 最好只用于外部的数据, 比如数据库
EnvironmentObject
Combine
它的核心概念是 Publishers 和 Subscribers
通过简单地在任意属性里添加注解 @Published 即可成为 Publisher . 它会自动同步 objectWillChange publisher
布局和展示
SwiftUI 使用 Flexible Box 布局系统(像 Web )
元素和修改器
Text("Hello World")
图片剪裁形状
Image("user")
.resizable()
.frame(width: 250, height: 250) .clipShape(Circle())
其他的看 API 文档
GeometryReader
struct ContentView: View {
var body: some View {
ScrollView {
HStack {
ForEach(0..<15){ index in GeometryReader { g in
Text("This is item: \(index)") .rotationEffect(.degrees(
Double(g.frame(in: .global).minX) ))
}
}.frame(width: 300, height: 300)
} }.background(Color.orange)
// .frame(width: 800, height: 800, alignment: .center)
}
}
画图和动画
Timer
传统上, 通过定时器来刷新画面
struct ContentView: View {
@State private var counter = 0
let timer = Timer.publish(every: 1, on: .current, in: .common).autoconnect()
var body: some View {
Text("Counter Ticks : \(counter)")
.onReceive(timer) { _ in
self.counter += 1
}
}
}
形状
Rectangle
struct ContentView: View {
var body: some View {
Rectangle()
.fill(Color.black)
.frame(width: 200, height: 200)
}
}
RoundedRectangle
struct ContentView: View {
var body: some View {
RoundedRectangle(cornerSize: CGSize.init(width: 35, height: 35))
.frame(width: 200, height: 200)
}
}
Circle
struct ContentView: View {
var body: some View {
Circle()
.frame(width: 200, height: 200)
}
}
Ellipse
struct ContentView: View {
var body: some View {
Ellipse()
.fill()
.frame(width: 200, height: 200)
}
}
Capsule
struct ContentView: View {
var body: some View {
Capsule()
.fill()
.frame(width: 200, height: 200)
}
}
形状修改器
Frame
修改形状的大小. 它会创建固定大小的形状
Clipped
限制内容并剪辑它. 可确保内容是容器的大小, 不会溢出
Trim
根据点参数 from, to 剪掉指定形状. 比如对于圆形来说
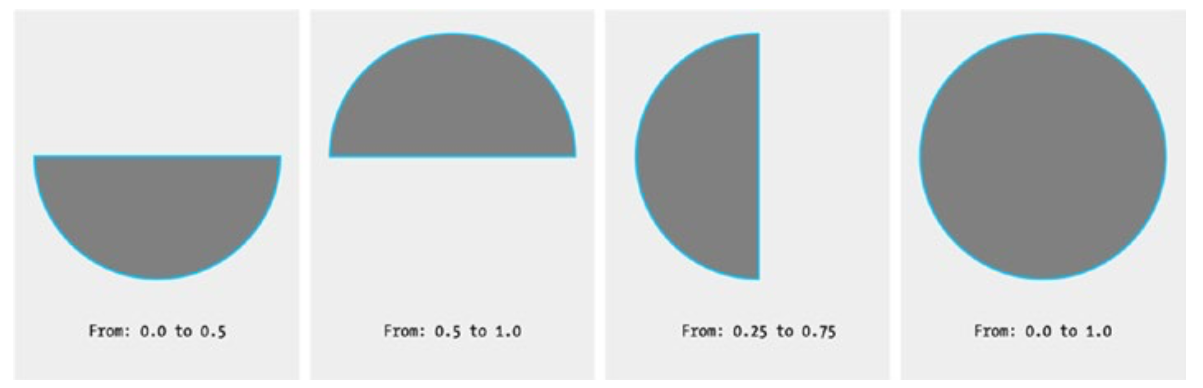
Stroke
struct ContentView: View {
var body: some View {
Rectangle()
.stroke(lineWidth: CGFloat.init(10.0))
.fill(Color.red)
}
}
LineJoin / LineCap / DashPhase
struct ContentView: View {
var body: some View {
Rectangle()
.stroke(style: StrokeStyle(
lineWidth: 2, lineCap: .round, lineJoin: .round, dash: [0, 5], dashPhase: 0
) )
.frame(width: 200, height: 200)
}
}
动画
struct ContentView: View {
@State private var jiggle = false
var body: some View {
Text("Hello World!")
.scaleEffect(jiggle ? 1.0 : 0.3)
.animation(Animation.spring().repeatForever())
.onAppear() {
self.jiggle.toggle()
}
.frame(width: 200, height: 200, alignment: .center)
}
}
Path
struct ContentView: View {
var body: some View {
Path { path in
path.move(to: CGPoint(x: 10, y: 10))
path.addLine(to: CGPoint(x: 10, y: 210))
path.addLine(to: CGPoint(x: 210, y: 210))
path.addLine(to: CGPoint(x: 210, y: 10))
}
.frame(width: 400, height: 400, alignment: .center)
}
}
交互
Tap
点击
struct ContentView: View {
var body: some View {
Text("Hello World!")
.onTapGesture {
print("Text was tapped")
}
.frame(width: 400, height: 400, alignment: .center)
}
}
LongPress
长按
struct ContentView: View {
var body: some View {
Text("Hello World!")
.onLongPressGesture() {
print("Text was long press")
}
.frame(width: 400, height: 400, alignment: .center)
}
}
Drag
拖动
struct ContentView: View {
var body: some View {
Text("Hello World!")
.gesture(
DragGesture(minimumDistance: 60)
.onEnded { drag in
print(drag)
}
)
.frame(width: 400, height: 400, alignment: .center)
}
}
Rotation
.gesture( RotationGesture( minimumAngleDelta: Angle. degrees(1))
Hover
struct ContentView: View {
var body: some View {
Text("Hello World")
.onHover{ _ in print("Hovering over the element")}
.frame(width: 400, height: 400, alignment: .center)
}
}
Appearing / Disappearing
.onAppear {
print("The view has appeared on screen")
}
.onDisappear {
print("The view has appeared on screen")
}
当 view 做准备显示到屏幕/关闭显示时触发
访问 API 数据
访问 URL
import Cocoa
let url = "https://icanhazdadjoke.com/"
var urlRequest = URLRequest(url: URL.init(string: url)!)
urlRequest.addValue("text/plain",
forHTTPHeaderField: "Accept")
URLSession.shared.dataTask(with: urlRequest) { data, response, error in
if let data = data,
let httpResponse = response as? HTTPURLResponse, (200..<300) ~= httpResponse.statusCode,
let strData = String(bytes: data, encoding: .utf8)
{
print(strData)
} }.resume()
处理 JSON
struct Joke: Codable {
var id: String
var joke: String
var status: Int
}
let json = try? JSONDecoder().decode(Joke.self, from: data) {
print(json)
}