<Swift编程权威指南>读书
Contents
基础注意
常量和变量
// 变量声明
var
//常量声明
let
比较
要特别注意浮点数的精确比较
=== : 两个实例是否指向同一个引用
!== : 两个实例是否不指向同一个引用
操作符
// 溢出操作符. 默认情况下是触发陷阱(不同其他编程语言, 默认是折回)
&+
&-
&*
switch
// 默认 case 会自动中断. 除非显式指定 fallthrough
import Cocoa
var errorCode:Int = 404
var errorMessage: String = "The request failed: "
switch errorCode {
case 404, 403:
errorMessage = "Sth wrong.."
fallthrough
default:
errorMessage += " please try again and review"
}
print(errorMessage)
值绑定
import Cocoa
var errorCode:Int = 500
var errorMessage: String = "The request failed: "
switch errorCode {
case 404, 403:
errorMessage = "Sth wrong.."
case let unkownCode:
errorMessage += " please try again and review. code = \(unkownCode)"
}
区间
valueX...valueY
元组
let err = (statusCode, errorString)
err.0
err.1
// 起别名
let err = (code: statusCode, error: errorString)
err.code
err.error
//结合 switch
import Cocoa
let firstCode = 404
let secondCode = 405
let error = (firstCode, secondCode)
switch error {
case (404, 404):
print("no items found")
case (404, _):
print("first item not found")
case (_, 404):
print("second item not found")
default:
print("all items found")
}
if case
单个 switch 分支优雅替代
import Cocoa
let age = 25
if case 18...35 = age, age >= 21 {
print("cool... \(age)")
}
字符串
组成字符串的字符都是 Character 类型, Character 表示 Unicode 字符.
Unicode 标量(unicode scalar, 一个标量对应某种给定语言中的一个基本字符).
而字符, 是由一个或多个 Unicode 标量构成的, 是因为还存在组合标量 (combining scalar)
即
String = 多个 Character 组成
Character = 一个或多个标量组成
// U+1F60E
let cool = "\u{1F60E}"
// 组合标量, 一个字符 á
let aAcute = "\u{0061}\u0301"
//查看字符的标量
import Cocoa
let aAcute = "\u{0061}\u{0301}"
for c in aAcute {
for s in c.unicodeScalars {
print("s => \(s.value)")
}
}
标准等价
Unicode 为某些常见的字符已提供组合过的形式. 这在 Swift 中, 组合后的和组合的是等价的(即使是在统计字符个数上也是等价的). 例如
import Cocoa
let aAcute = "\u{0061}\u{0301}"
let aAcuteCombind = "\u{00E1}"
print(aAcute == aAcuteCombind)
索引
import Cocoa
let hello = "hello world"
let start = hello.startIndex
let end = hello.index(start, offsetBy: 4)
let result = hello[end]
print(result)
不能直接使用 Int 作为索引
Optional
import Cocoa
var hello: String?
hello = "hello world"
print(hello)
// Optional("hello world")
// 注意先判断 nil . 然后获取值. !
print(hello!)
空绑定
import Cocoa
var hello: String?
//hello = "hello world"
if let v = hello {
print(v)
} else {
print("no value...")
}
nil 合并运算符
var hello: String?
let des = hello ?? "default des"
如果 hello 是 optional 类型, 以及 hello 为 nil 则 des 为 “default des” , 否则是 hello 的值
数组
var hello: [String]
var hello: Array<String>
import Cocoa
var hello: Array<String> = []
print(hello)
hello.append("hello")
hello.append("world")
print(hello)
hello.remove(at: 1)
print(hello)
// 取范围
hello[0...1]
// 修改
hello[0] = "new value"
//拼接两个数组
hello += ["new", "value"]
字典
键必须是 hashtable 的(可散列的)
import Cocoa
var dic1: Dictionary<String, Double> = [:]
var dic2 = Dictionary<String, Double>()
var dic3: [String:Double] = [:]
var dic4 = [String:Double]()
// 字典变数组
let arr = Array(dic1.keys)
// 遍历
for (k, v) in dic1 {
}
集合
var aSet = Set<String>()
var bSet: Set = ["hello", "world"]
可进行并, 交, 差处理
函数
参数名
func hello(to name:String) {
}
//带默认值
import Cocoa
func helloWorld(to name: String = "default") {
print(name)
}
helloWorld()
// 返回值
import Cocoa
func sayHello(to name: String) -> String {
return "hello \(name)"
}
print(sayHello(to: "fuck"))
// 多个返回值的话, 利用元组
//返回 Optional 类型
func sayHello(to name: String) -> String? {
}
- to 是调用者使用的名字
- name 是函数内部使用的名字
in-out 参数
修改参数的值
import Cocoa
func helloWorld(to name: inout String) {
print(name)
name = "new value"
}
var hello = "hello world"
helloWorld(to: &hello)
print(hello)
函数类型
由函数参数和返回值组成. 示例
([Int]) -> ([Int], [Int])
闭包
{(paramters) -> returnType in
//代码
}
例如
import Cocoa
let v = [1,3,2, 4, 5, 999, 10, 88]
let sorted = v.sorted(by: {
(i: Int, j: Int) -> Bool in
return i < j
})
print(sorted)
//再简
let sorted = v.sorted(by: {
i, j in i < j
})
//再简
let sorted = v.sorted(by: {
$0 < $1
})
闭包是一种引用类型
高阶函数
- map
- filter
- reduce
枚举
// 定义
import Cocoa
enum TextAlignment {
case left
case right
case center
}
原始值
import Cocoa
enum TextAlignment: Int {
case left
case right
case center
}
// 2
print(TextAlignment.center.rawValue)
// 从原始值 -> enum . 这种是 optional 类型
print(TextAlignment(rawValue: 1))
// 增加函数
import Cocoa
enum TextAlignment: Int {
case left
case right
case center
func sayHello(name: String) -> String {
return "\(self) : say \(name)"
}
}
print(TextAlignment.center.sayHello(name: "hello "))
// 递归枚举
indirect enum Hello {
}
结构体和类
struct Town {
var population = 5_422
var numberOfStopLights = 4
func showDes() {
print("population: \(population), number of stoplights: \(numberOfStopLights)")
}
mutating func addPopulation(delta: Int) {
population += delta
}
}
myTown.showDes()
myTown.addPopulation(delta: 10)
myTown.showDes()
mutating 方法
如果实例方法要修改结构体的属性, 则要标记为 mutating
类
class Monster {
var town: Town?
var name = "Monster"
func terrorizeTown() {
if town != nil {
print("\(name) is terrorizing a town!")
} else {
print("\(name) hasn't found a town to terrorize yet...!")
}
}
}
var myTown = Town()
var monster = Monster()
monster.town = myTown
monster.terrorizeTown()
类可以继承, 但结构体没有
属性
类, 结构体和枚举, 都可以有属性.
属性为两种
存储属性 : 可有默认值- 可读/写
var - 可只读
let - 惰性:
lazy var
- 可读/写
计算属性: 观察属性的变化, 并在属性赋新值时执行特定的代码- 读
get - 写
set
- 读
属性观察者
willSet: 观察属性即将发生的变化(参数是新值)didSet: 观察属性已发生的变化(参数是旧值)
类型属性
值类型属性 static
struct Town {
static let region = "south"
}
子类不能覆盖父类的类型属性. 如果子类能为某个属性提供自己的实现, 那就是 class 关键字
ACL
从上到下依次减小访问范围
- open : 对模块内的所有文件以及引入了该模块的文件都可见, 并可继承
- public : 对模块内的所有文件以及引入了该模块的文件都可见
- internal (默认) : 对模块内的文件可见
- fileprivate : 只对所在源文件可见
- private : 只对所在的作用域可见
初始化
struct Hello {
var hello: String
var age: Int
init(someValue: String) {
self.init(a: 10)
self.hello = "\(someValue) : init"
}
init(a: Int) {
age = a
hello = "no name"
}
}
var h = Hello(a: 10)
print(h.hello)
类的必须初始化方法
class Monster {
required init(paramter) {
//code
}
}
反初始化
deinit
class Monster {
required init(paramter) {
//code
}
deinit {
//code
}
}
可失败的初始化
class Monster {
init?(paramter) {
if xxx {
return nil
}
//code
}
}
值类型与引用类型
值类型总是被复制. Swift 基本类型 (Array, Dictionary, Int, String) 都是用结构体实现的, 它们都是 值类型
应该尽量优先使用 struct 来实现数据建模. 必要时才用 class
引用类型class: 赋值给常量或变量时, 这时得到的就是实例的引用. 对引用来说, 常量或变量都指向内存中的同一个实例.
复制
在 swift 中, 没有提供深复制. 这意味着, swift 中的复制是浅复制.(即, 表示只复制实例的引用)
相等与同一
- equals
- identify
写时复制
Swift 标准库中的值类型都实现了写时复制的机制
Swift 的容器也默认提供了写时复制, 只要 元素都是实现了写时复制的话
协议
能让你定义类型需要满足的接口. 满足某个协议的类型, 称为符合 conform 这个协议
import Cocoa
protocol DS {
var rows: Int {get}
var cols: Int {get}
}
struct MySQL: DS {
var rows: Int {
return 10
}
var cols: Int {
return 20
}
}
var m = MySQL()
print(m.cols)
- 所有的类型都可以符合协议
- 一个类型也可以符合多个协议
协议继承
继承另一个协议要求符合的类型提供它本身及其所继承协议的所有属性和方法
协议扩展
extension ProtocolName {
//code
}
错误处理
do {
try ...
} catch xxxError(param) {
} catch {
//除上面的 cathc 处理之外的所有错误
}
扩展
import Cocoa
typealias newDouble = Double
extension newDouble {
var hello: newDouble {
return self * 3.14
}
}
var hello:newDouble = 1.0
print(hello.hello)
泛型
struct Stack<Element> {
var items = [Element]()
mutating func push(_ newItem: Element) {
items.append(newItem)
}
mutating func pop() -> Element? {
guard !items.isEmpty else {
return nil
}
retun items.removeLast()
}
}
泛型函数
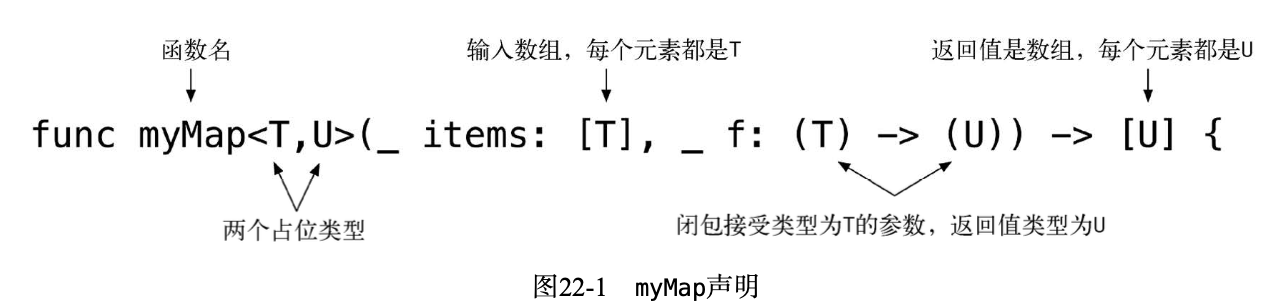
类型约束
func checkIfEqual<T: Equatable>(_ first: T, _ second: T) -> Bool {
return first == second
}
关联类型协议
public protocol IteratorProtocol {
associatedtype Element
mutating func next() -> Self.Element?
}
符合这个协议的类型应该在其定义内部为 Element 提供 typealias 定义
struct StackIterator<T>: IteratorProtocol {
typealias Element = T
var stack: Stack<T>
mutating func next() -> Element? {
return stack.pop()
}
}
// Swift 也可自动推断, 所以 typealias 可简化
struct StackIterator<T>: IteratorProtocol {
var stack: Stack<T>
mutating func next() -> T? {
return stack.pop()
}
}
内存管理
值类型数据这个没问题
引用类型: 为每个类实例维护一个引用计数. > 0 实例就会存活, = 0 , 实例就会回收, deinit 方法运行
Swift 使用的是自动引用计数. ARC
强循环引用: 可能会导致内在泄漏
- 手动解决: 将某对象的引用设置为 nil 后, 马上遍历它拥有的对象引用并将所有者设置为 nil
用 weak 自动打破强循环引用
- 必须用 var 声明, 而不能用 let
- 弱引用必须声明为可空类型 optional
Equatable 和 Comparable
struct Point: Equatable {
let x: Int
let y: Int
static func ==(lhs: Point, rhs: Point) -> Bool { return (lhs.x == rhs.x) && (lhs.y == rhs.y)
}
}
